Air compressors are essential for powering pneumatic tools. You can choose the right size and type for your specific needs by understanding the basics of air compressors and how they work.
Proper setup and maintenance are crucial to ensure optimal performance. If you’ve ever wondered how to use an air compressor for powering pneumatic tools. Here we will walk you through everything you need to know to use an air compressor for powering pneumatic tools.
From selecting the right air compressor for your needs to connecting it to your tools and adjusting the pressure, we’ve got you covered. We’ll also dive into important safety precautions and maintenance tips to keep your air compressor running smoothly. Plus, we’ll provide troubleshooting solutions for common problems that may arise. Get ready to unleash the power of pneumatic tools with confidence!

How To Use An Air Compressor For Powering Pneumatic Tools – 6 Steps
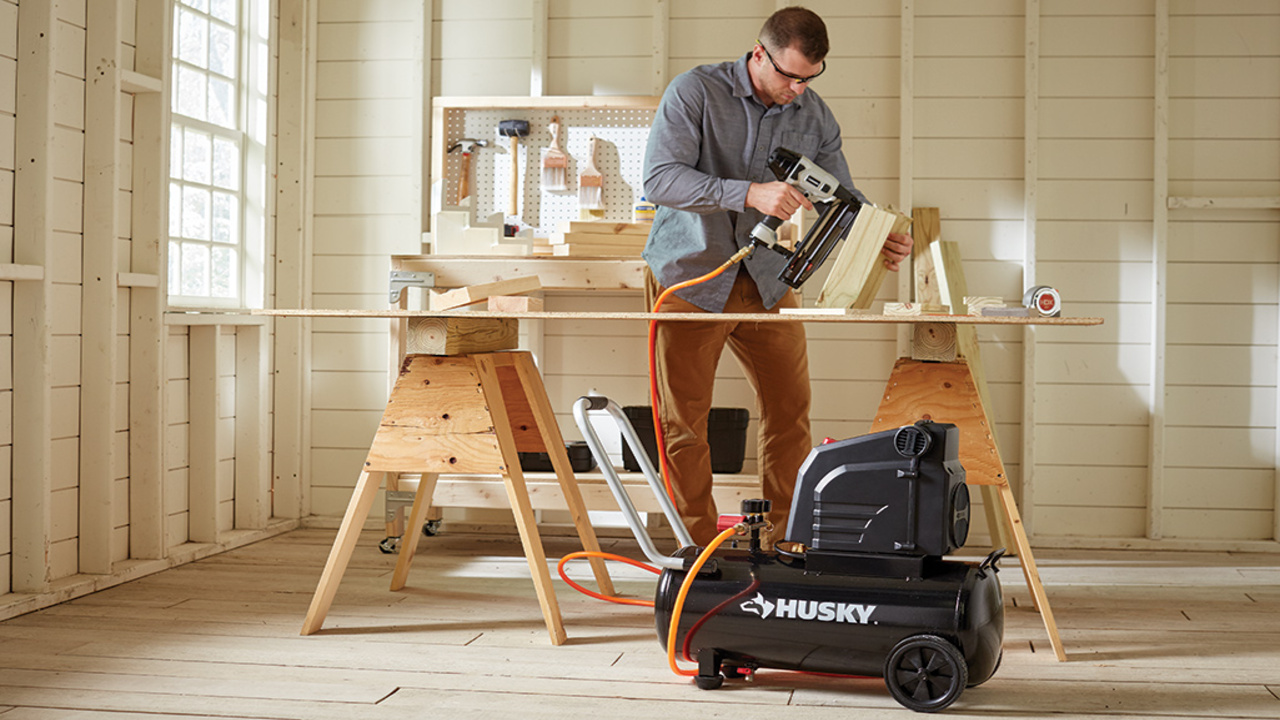

Understand the basics of air compressors and pneumatic tools. Choose the right size and type of air compressor for your tools. Set up and maintain your air compressor properly for optimal performance. Connect your pneumatic tools to the air compressor using the appropriate fittings.
Use proper safety precautions when operating pneumatic tools with an air compressor. Here are the full process on how to use an air compressor for powering pneumatic tools.
1. Selecting The Right Air Compressor

When selecting the right air compressor for powering pneumatic tools, there are several factors to consider. First, you should determine the power requirements of your tools and choose an air compressor with sufficient horsepower and CFM (cubic feet per minute) rating.
Additionally, you need to decide if you require a portable or stationary compressor based on your workspace and mobility needs. It’s also important to check the tank size, as a larger tank provides longer tool run times. Features like adjustable pressure settings, gauges, and safety valves should also be considered. Lastly, ensure that the compressor has proper maintenance and safety protocols in place.
2. Connecting The Air Compressor To The Tool
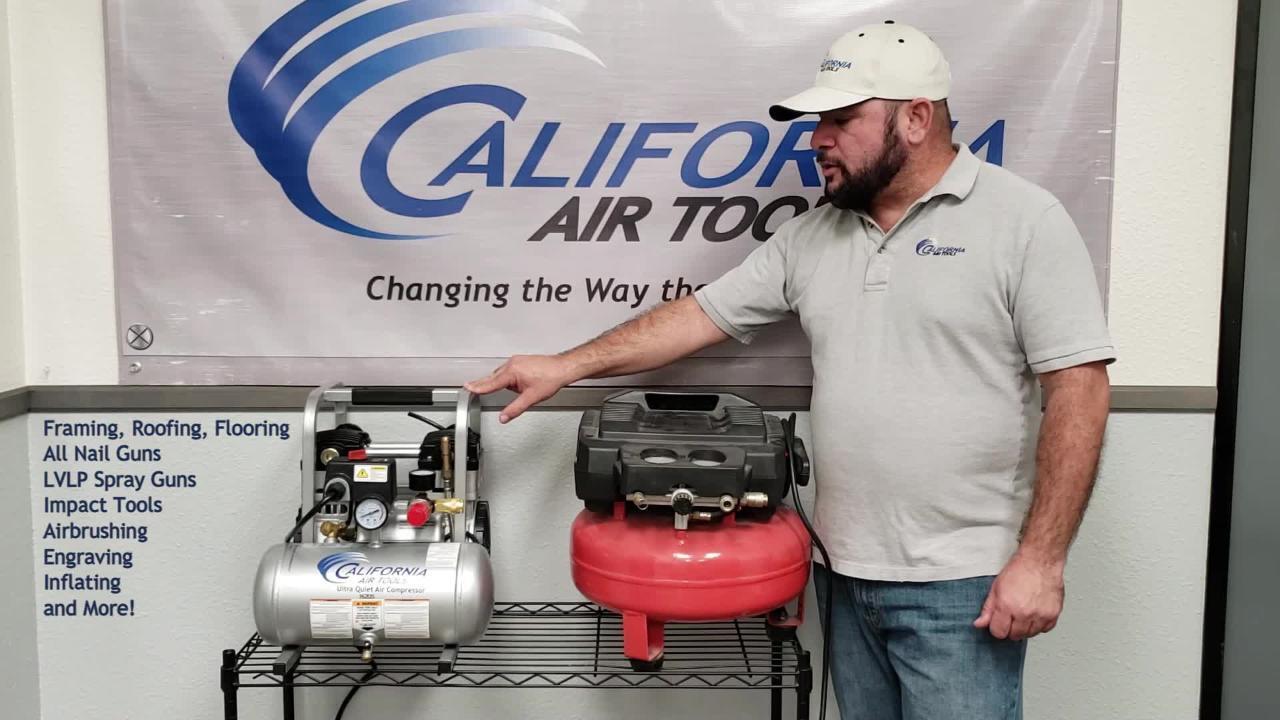

Before connecting the air compressor to a pneumatic tool, ensure compatibility in terms of air pressure requirements. Attach the appropriate hose or connector securely to the air compressor’s outlet port. Follow the tool’s user manual for specific instructions on connecting it to the air compressor.
Turn on the compressor and allow it to reach the recommended pressure level. Test the tool by engaging its power switch, ensuring proper functionality. Adjust the air pressure using the compressor’s regulator if needed.
3. Adjusting The Air Compressor Pressure
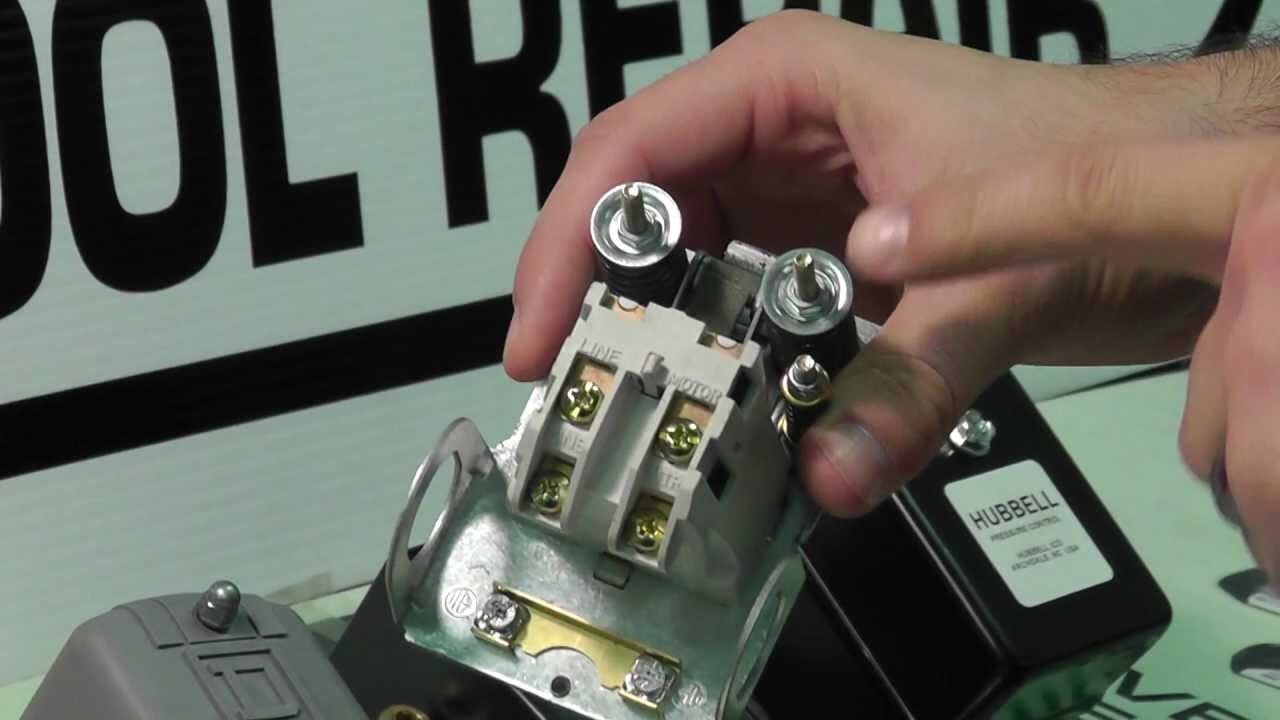
Before using an air compressor, it’s crucial to adjust the pressure according to your pneumatic tool requirements. Check the recommended operating pressure for each tool in the user manual. Locate the pressure regulator, typically a knob or dial on the compressor, and turn off the device before making adjustments.
Increase the pressure by turning the regulator clockwise and decrease it counterclockwise. Gradually increase the pressure while monitoring the gauge until you achieve the desired level.
4. Understanding The Safety Precautions
Before using an air compressor, it is essential to familiarize yourself with the safety precautions outlined in the user manual. Ensure that the compressor is properly grounded and all electrical connections are secure. When operating pneumatic tools, it is important to use appropriate personal protective equipment, such as safety glasses and ear protection.
Check the air pressure gauge on the compressor to ensure it is set at the correct level for your specific tool. Connect the tool to the compressor using a hose and secure it tightly with the appropriate fittings. Turn on the compressor and allow it to build up pressure before using the tool.
5.Maintaining The Air Compressor
To keep your air compressor in optimal condition, there are a few key maintenance tasks you should regularly perform. First, make sure to regularly check and clean the air filter to prevent dust and debris from damaging the compressor. Secondly, monitor the oil level and change it as recommended by the manufacturer to ensure optimal performance. Additionally, be sure to drain any moisture that collects in the tank to prevent corrosion.
Use a pressure regulator to adjust the air pressure based on the requirements of your pneumatic tools, and always connect tools securely to the compressor with the appropriate fittings and hoses, checking for leaks or obstructions. Finally, start the compressor and allow it to build up pressure before using your pneumatic tools.
6. Working With Different Types Of Pneumatic Tools
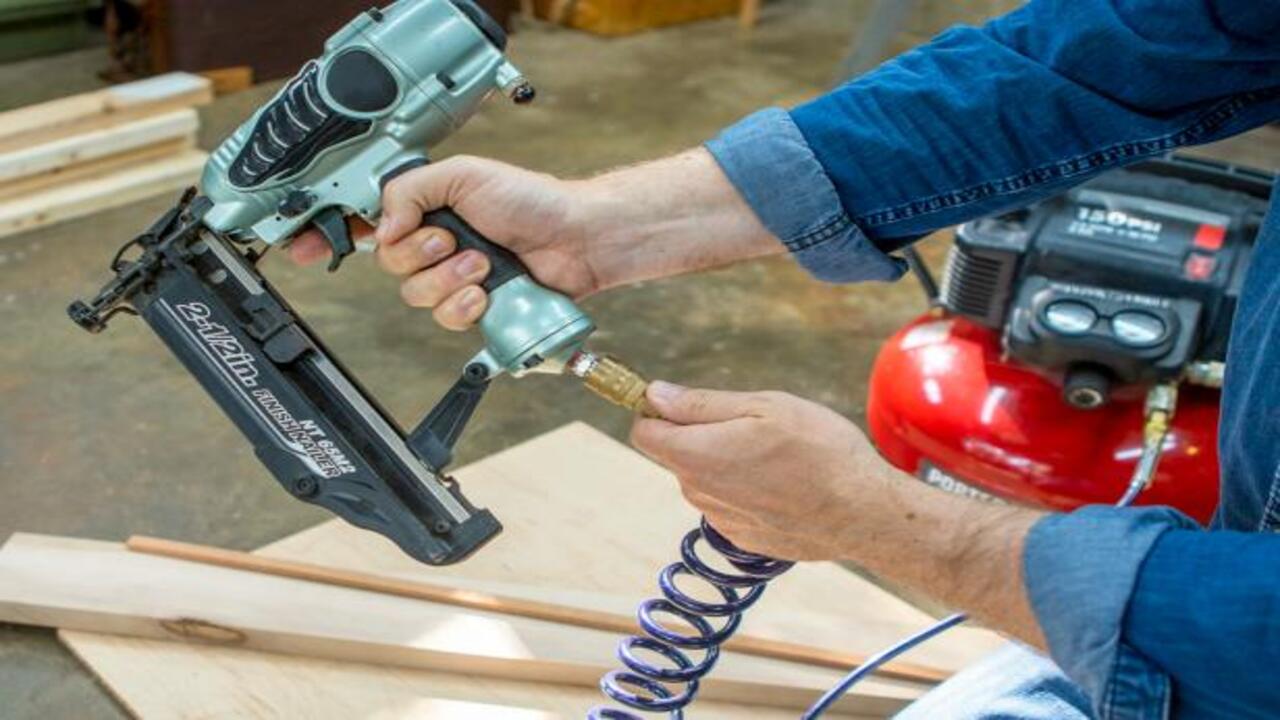

Pneumatic tools rely on compressed air from an air compressor to function. Different types of pneumatic tools require different levels of air pressure, so it’s important to adjust the compressor accordingly. Before connecting a pneumatic tool, make sure the air compressor is turned off and the pressure has been released.
Connect the tool to the air hose using the appropriate connectors or fittings. Adjust the pressure regulator on the compressor to match the recommended pressure for the specific tool. Turn on the compressor and allow it to build up enough pressure before using the tool.
Air Compressor Safety Tips

When using an air compressor, it is important to prioritize safety. Start by reading and following the manufacturer’s instructions for operating the compressor. Always wear appropriate safety gear, such as safety glasses and ear protection.
Ensure that the compressor is properly grounded to avoid electrical shocks. Regularly inspect and maintain the compressor to keep it in good working condition. Never exceed the maximum pressure rating or use it for purposes it is not designed for. Lastly, keep children and pets away from the area where the compressor is being used.
Tips To Make The Most Of Your Air Compressor
To make the most of your air compressor, it is essential to understand its capacity and capabilities. Use the appropriate attachments and fittings for your pneumatic tools to ensure a secure and efficient connection.
Regularly check and maintain your air compressor, including monitoring air pressure and adjusting it for each specific task. Always follow safety guidelines, such as wearing protective gear and securing tools properly. By following these tips, you can maximize the performance and longevity of your air compressor.
Troubleshooting Common Air Compressor Problems

Troubleshooting common air compressor problems can help ensure optimal performance and prevent costly repairs. Low air pressure may be due to leaks, dirty filters, or an improperly sized compressor. Excessive noise could indicate loose components, worn parts, or lack of lubrication.
Prevent overheating by checking ventilation, oil levels, and intake filters. Inspecting hoses, fittings, and connections for air leaks is essential. Inconsistent pressure may require checking for clogs, adjusting the regulator, and proper maintenance. By addressing these issues, you can keep your air compressor running smoothly and extend its lifespan.
Maintaining Your Air Compressor

To ensure optimal performance, regularly check and replace air filters. Prevent rust and damage by draining moisture from the compressor’s tank. Inspect and tighten connections to prevent air leaks. Keep the compressor clean by removing dirt and debris. Follow manufacturer guidelines for oil changes and lubrication to prolong its life.
Conclusion
Becoming proficient in utilizing air compressors to power pneumatic tools can significantly improve the efficiency and efficacy of your work. By carefully choosing an appropriate air compressor, correctly connecting it to your tools, adjusting the pressure as needed, and adhering to safety guidelines, you can ensure optimal performance and extend the lifespan of your equipment.
Routine maintenance and troubleshooting are also crucial in preventing common issues and keeping your air compressor in optimal condition. Stay safe while making the most out of your pneumatic tools. Hope the above outline on how to use an air compressor for powering pneumatic tools will be very helpful for your.
Frequently Asked Questions
1.Can You Use Air Tools With An Air Compressor?
Ans: Yes, air tools are designed to be used with an air compressor. Air compressors provide the power and pressure needed to operate pneumatic tools. Ensure a secure connection between the tool and air hose, and adjust the pressure as required.
2.What Size Air Compressor Do I Need To Power Air Tools?
Ans: To determine the size of air compressor you need for your air tools, consider the CFM rating, maximum PSI requirement, and tank size. Check the manufacturer’s guidelines or seek professional advice for accurate sizing based on your specific tools.
3.Will A 30 Gallon Air Compressor Run An Impact Wrench?
Ans: A 30-gallon air compressor is generally capable of running most impact wrenches, but it’s important to verify that the compressor can deliver the required CFM and PSI as specified by the tool.
4.What Size Air Compressor Do I Need To Run Air Tools?
Ans: The size of the air compressor you need will vary based on the air tools you intend to use. Refer to the manufacturer’s specifications for the required CFM and PSI ratings. In general, a small compressor with a 20-30 gallon tank is suitable for most home projects, while heavy-duty or professional use may require a larger compressor with a higher CFM rating.
5.What Is The Best Handheld Portable Air Compressor For?
Ans: The ideal handheld portable air compressor is versatile and can be used for inflating tires, sports equipment, inflatable toys, and air mattresses. It’s also handy for powering pneumatic tools like nail guns, staplers, and paint sprayers.