If you suspect that your small block Chevy (SBC) engine is suffering from low compression, then it’s essential to know how to check SBC head compression.
The first step is to remove all the spark plugs to allow the engine to spin freely. Next, screw the compression tester into the spark plug hole of the first cylinder and crank the engine for a few seconds.
The compression gauge will show the pressure reading for that cylinder. Repeat the process for each cylinder and record the results. The compression readings should be within 10% of each other.
If the reading is low, it could indicate a problem with the valves, piston rings, or head gasket. If the cylinder readings are consistently low, it may be necessary to remove the cylinder head to inspect the valves and the cylinder walls. A compression test is a quick and easy way to diagnose engine problems, saving you time and money in the long run.

Symptoms Of Head Compression Issues
Head compression issues can cause a range of symptoms that can be concerning and even debilitating if left untreated. Some of the most common symptoms of head compression issues include headaches, dizziness, difficulty concentrating, memory problems, and changes in vision or hearing.
Additionally, some individuals may experience tingling or numbness in their limbs, facial weakness, or difficulty with balance and coordination. These symptoms can vary in severity and duration depending on the underlying cause of the head compression issue.
For example, a brain tumour may cause more severe symptoms that worsen over time, while a concussion may lead to more immediate symptoms that gradually improve. It is essential to seek medical attention if you are experiencing any of these symptoms, as early detection and treatment can be crucial in preventing further complications.
A qualified healthcare provider can perform a thorough evaluation to determine the cause of your symptoms and recommend the appropriate course of treatment. Surgery may sometimes be necessary to relieve the compression and alleviate the associated symptoms.
Tools Needed For Checking Compression

- Compression Tester: This is the primary tool used to measure engine compression. It consists of a pressure gauge connected to a threaded adapter that can be screwed into the spark plug hole. The gauge measures the pressure generated by the engine during compression.
- Spark Plug Socket and Ratchet: You’ll need a spark plug socket and a ratchet to remove the spark plugs from the engine. This allows access for the compression tester to be attached.
- Socket Extension: A socket extension may be required to reach spark plugs located in deep recesses.
- Rubber Hose or Adapter: Some compression testers have a rubber hose or adapter connecting the compression tester to the spark plug hole. This provides a better seal and ensures accurate readings.
- Battery or External Power Source: Depending on the type of compression tester, you may need a battery or an external power source to operate the gauge.
- Safety Gear: It’s always recommended to wear safety goggles and gloves while working on an engine to protect yourself from any potential hazards.
How To Check Sbc Head Compression – A Guideline

Check the compression of SBC (Small Block Chevy) heads; you will need a compression gauge. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to perform a compression test on SBC heads:
Step 1: Locate Spark Plug Holes

Identify the spark plug holes on the SBC heads. There will be one hole per cylinder.
Step 2: Remove Spark Plugs
Using a socket set, carefully remove all the spark plugs from the SBC heads. Make sure to keep them in order.
Step 3: Disable Ignition System
To prevent the engine from starting during the compression test, disable the ignition system. This can be done by disconnecting the ignition coil or ignition module.
Step 4: Compression Gauge Setup
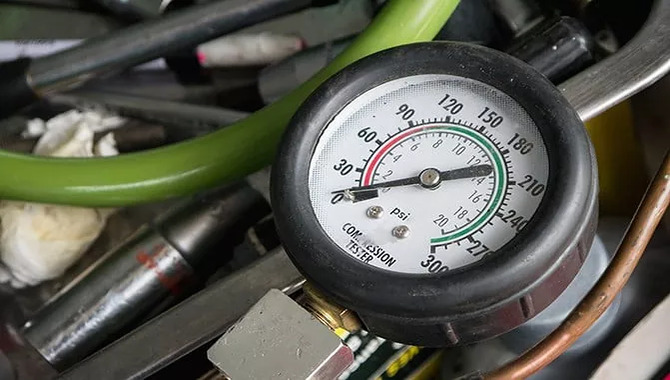
Select the appropriate adapter for your compression gauge and attach it to the end of the gauge hose. Then, insert the gauge hose into the spark plug hole for cylinder number one.
Step 5: Crank The Engine
Ask a helper to crank the engine by turning the ignition key or using a remote starter switch. Allow the engine to crank for a few seconds, typically five to eight revolutions.
Step 6: Record Compression Reading

Observe the compression gauge and note the reading on the scale when the needle stabilizes. Repeat this process for each cylinder, recording the compression readings for each one.
Step 7: Repeat For All Cylinders
Repeat steps 5 to 7 for each cylinder on the SBC heads, ensuring that the spark plug hole and adapter are changed accordingly.
Step 8: Analyze Results
Compare the compression readings for each cylinder. The readings should be relatively close to each other.
Step 9: Reinstall Spark Plugs

After completing the compression test, reinstall the spark plugs into their respective cylinders. Ensure they are tightened to the manufacturer’s specifications.
Understanding Compression Readings
Understanding compression readings is essential for maintaining the health and longevity of any engine. Compression readings measure the pressure the engine’s pistons produce during the compression stroke.
This reading is a critical indicator of engine health, determining whether the engine produces enough pressure to operate efficiently. A compression reading that is too low may indicate worn or damaged piston rings, valves, or cylinder walls, while a reading that is too high may indicate carbon buildup or a faulty head gasket.
To accurately interpret compression readings, it is important to have a basic understanding of engine mechanics and the compression process. Typically, compression readings are taken using a compression gauge inserted into each cylinder’s spark plug hole.
The engine is cranked over several times, and the gauge displays the pressure reading. By comparing these readings to the manufacturer’s specifications, mechanics can determine whether the engine operates within acceptable parameters.
Troubleshooting Compression Problems

Regarding video production, compression problems can be a real headache. These issues can significantly affect the final product, whether it’s slow rendering times or poor video quality. Fortunately, several troubleshooting techniques can help resolve such problems.
One of the first things to check is the video compression settings. Ensure that the settings are appropriate for the type of project and intended output. If the compression settings are correct but the video quality is still poor, try adjusting the bit or frame rate.
Additionally, it’s important to remember that sometimes hardware or software issues can cause compression problems. Check to see if any updates or patches are available for the software, and ensure that the computer hardware meets the minimum requirements for video production.
Other factors, such as the file format, resolution, and colour space, can also impact video compression. By troubleshooting these issues, video producers can avoid compression problems and ensure that their final product meets the highest standards of quality.
Common Causes Of Head Compression Issues
Head compression issues can be caused by a number of different factors. One of the most common causes is physical trauma, such as a blow to the head or a whiplash injury. In these cases, the compression may be caused by swelling or bleeding in the brain or surrounding tissues.
Another common cause of head compression is a tumour or other growth in the brain. This can put pressure on the surrounding tissues, leading to symptoms such as headaches, dizziness, and difficulty concentrating.
Other possible causes of head compression include infections, such as meningitis or encephalitis, and cardiovascular issues, such as high blood pressure or atherosclerosis. In some cases, head compression may also be a symptom of a more general health condition, such as diabetes or thyroid disease.
Regardless of the underlying cause, it is important to seek medical attention if you are experiencing symptoms of head compression, as prompt diagnosis and treatment can help minimize the risk of serious complications.
When To Seek Professional Help
It’s important to understand that there’s no shame in admitting that you need support. In fact, recognizing when to seek professional help can be a sign of strength, not weakness. If you’re struggling with a mental health issue, such as depression or anxiety, it’s important to know that you don’t have to suffer alone.
Seeking the help of a licensed therapist or mental health professional can provide you with the support and guidance you need to overcome your challenges. There are a variety of signs that may indicate it’s time to seek professional help.
For example, if you’re experiencing persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, or worthlessness, it may be a sign that you’re struggling with depression. If you’re having trouble sleeping, concentrating, or enjoying things you used to love, it may be a sign of a more serious mental health issue.
Conclusion
Knowing how to check SBC head compression is a crucial task that requires attention to detail and precision. Using the step-by-step guide outlined in this blog post, you can perform this task with ease and confidence. Remember to follow all safety precautions and take your time during the process.
Regularly checking the head compression can help you identify issues early on and save you from costly repairs in the future. With a little practice, you can become a pro at checking the head compression on your SBC engine.
FAQ
1.Why Is It Important To Check SBC Head Compression?
Ans: Checking SBC head compression is crucial to determine the health and performance of the engine. It helps identify potential issues such as blown head gaskets, , or piston ring wear.
2.How Do I Prepare The Engine For Compression Testing?
Ans: Start by ensuring the engine is warm and at operating temperature. Remove the spark plugs and disconnect the ignition coil to prevent the engine from starting during the test.
3.How Do I Prepare The Engine For Compression Testing?
Ans: Start by ensuring the engine is warm and at operating temperature. Remove the spark plugs and disconnect the ignition coil to prevent the engine from starting during the test.
4.How Do I Interpret Uneven Compression Readings Across Cylinders?
Ans: Significant variations in compression readings between cylinders may indicate valve or head gasket problems. Consult a professional mechanic to diagnose and resolve the issue.
5.What Is The Acceptable Compression Range For SBC Heads?
Ans: Generally, a healthy SBC engine should have compression readings between 140 and 160 psi, but refer to the engine’s specifications or service manual for the recommended range.